|
Total Daily Energy Expenditure (TDEE) is the total amount of energy that our body burns in a day, including all physical activities, digestion, and metabolism. It is an essential factor to consider when setting weight loss and body composition goals. Understanding TDEE can help us determine how many calories we need to consume to maintain, gain, or lose weight.
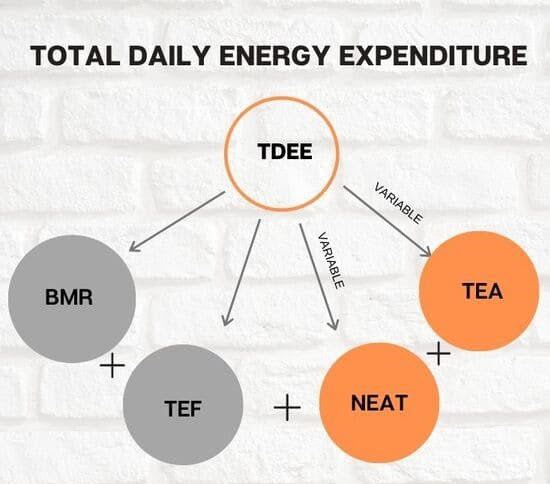
Calculating your TDEE is relatively simple. There are several online calculators such as one that we have on our Health Calculators page that can help you determine your TDEE based on your age, gender, height, weight, and activity level. However, it is essential to note that these calculators only provide an estimate, and your actual TDEE may vary based on individual factors such as genetics and metabolism. Once you have calculated your TDEE, you can use it to determine your daily calorie needs. If your goal is to lose weight, you will need to consume fewer calories than your TDEE, while if your goal is to gain weight, you will need to consume more calories than your TDEE. It is essential to note that a calorie deficit or surplus of 500-1000 calories per day is generally considered safe and effective for weight loss or gain. In addition to calorie intake, your TDEE can also help you determine how many calories you need to burn through exercise to achieve your goals. For example, if your TDEE is 2000 calories per day, and you want to lose one pound per week, you will need to create a calorie deficit of 3500 calories per week, or 500 calories per day. This deficit can be achieved through a combination of calorie restriction and exercise. TDEE is made up of four components: Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR), Thermic Effect of Feeding (TEF), Non-exercise activity thermogenesis (NEAT), and Thermic effect of activity (TEA). BMR is the amount of energy that our body burns at rest to maintain basic functions such as breathing, circulation, and organ function. This is the amount of calories utilized to simply function without eating or movement. It accounts for about 60-70% of our TDEE. It is very difficult to measure BMR so Resting Metabolic Rate (RMR) is often used. RMR is similar to BMR but is measured under less strict conditions, RMR is slightly higher than BMR due to the thermic effect of food. The best way to improve your BMR and RMR is through strength training, as muscle mass increases our metabolic rate. Cryotherapy has also been known to help increase metabolic rates. We are happy to offer Resting Metabolic rate testing as one of our services. TEF is the energy that our body uses to digest, absorb, and metabolize food. It accounts for about 10% of our TDEE. Protein has the highest thermic effect, followed by carbohydrates and fats. NEAT is the energy that we expend during non-exercise activities such as fidgeting, walking, and standing. It accounts for about 15-20% of our TDEE. Increasing NEAT can be an effective way to burn more calories throughout the day. TEA is the energy that we expend during exercise and physical activity. It accounts for about 10-15% of our TDEE. Increasing TEA can be an effective way to burn more calories and improve overall health. To enhance each component of TDEE for weight loss, we can make small changes to our daily routine. For example, increasing protein intake can increase the thermic effect of feeding. Taking frequent breaks to stand and stretch can increase NEAT. Incorporating strength training and high-intensity interval training (HIIT) can increase TEA. Changing our Body Composition can increase BMR. In conclusion, understanding TDEE is crucial for setting weight loss and body composition goals. By breaking down each component of TDEE and making small changes to our daily routine, we can enhance our TDEE and achieve our desired results. Remember, weight loss is not just about reducing calories, but also about increasing energy expenditure through a combination of diet and exercise. By focusing on TDEE, we can create a sustainable and effective weight loss plan that promotes overall health and well-being. It is important to note that while TDEE is a useful tool for nutrition and exercise planning, it is not the only factor to consider. Other factors, such as macronutrient ratios, meal timing, and exercise intensity, can also impact your weight and body composition goals. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine an appropriate calorie intake and exercise plan based on individual needs and goals.
0 Comments
Leave a Reply. |
AuthorDamian Solorzano is Health and Wellness Influencer, Respiratory Specialist and Health Coach who is passionate about optimizing personal health. Categories
All
Archives
March 2024
|
 RSS Feed
RSS Feed